IRS Form 1099-R Instructions
Taxpayers who take retirement distributions may receive IRS Form 1099-R in the January following the calendar year of their distribution. However, this tax form serves many purposes besides simply reporting retirement benefits.
In this article, we’ll walk through IRS Form 1099-R, including:
- A comprehensive look at what you should see in each box of this tax form
- Distribution codes that may apply and how to understand them
- Other frequently asked questions
Let’s start with a step by step look at IRS Form 1099-R.
Table of contents
IRS Form 1099-R Instructions
In most of our articles, we walk you through how to complete the tax form. However, most readers will probably want to understand the information reported on their IRS Form 1099-R, instead of how to complete it.
Before we start breaking down this form, it’s important to understand that there can be up to 6 copies of IRS Form 1099-R.
Here is a break down of where all these forms end up:
- Copy A: Internal Revenue Service Center
- Copy B: To be filed with recipient’s income tax return
- Copy C: For recipient’s tax records
- Copy D: For payer’s tax records
- Copy 1: For state, city, or local tax department
- Copy 2: To be filed with recipient’s state, city, or local tax return
For recipients who do not pay state, city, or local income tax, copies 1 and 2 are optional.
Let’s get into the form itself, starting with the payer and recipient information fields on the left side of the form.
Taxpayer information fields
In the boxes on the left side of the form, you should see your personal information, as well as the information for the financial institution, retirement benefits coordinator, or plan administrator.
Review these for accuracy, to make sure that the reported information is correct.
Payer’s information
This field should contain the following information with regards to the payer:
- Payer’s name
- Street address
- City, state, ZIP code
- Telephone number
If you have any questions about any of the transactions reported on this form, you should have enough contact information to reach out to the financial institution for resolution.
Payer’s TIN
Most likely, this will be an employer identification number, or EIN.
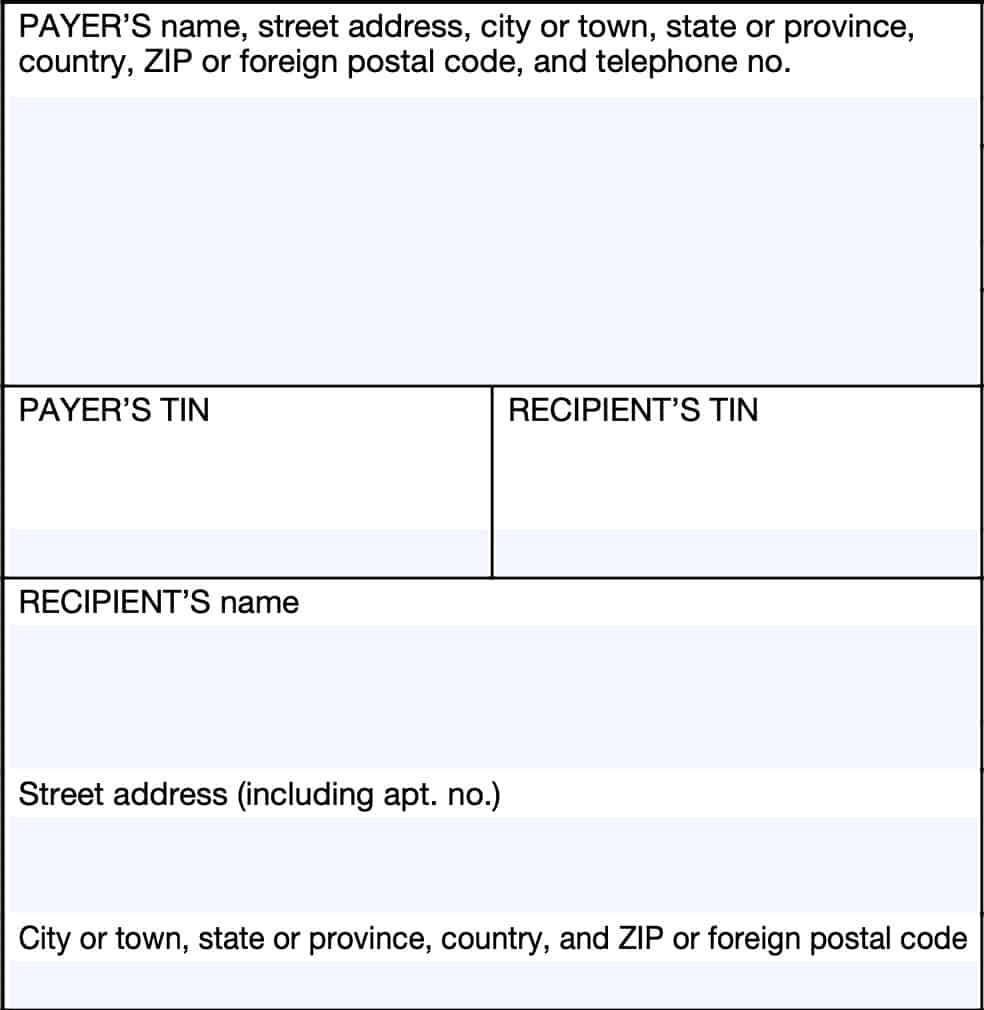
Recipient’s TIN
This field should contain your Social Security number, or SSN. Quickly review this field for accuracy.
Recipient’s information
This field should contain your name and complete mailing address. Review this for incorrect information.
Boxes 1 through 9
The right side of the 1099-R tax form contains Boxes 1 through 9. Let’s look a little more closely at each one.
Box 1: Gross distribution
You should find the total amount of pension benefits or account distribution in Box 1, before tax withholdings. This amount should include the following:
- Direct rollovers to or from an individual retirement account (IRA)
- IRA direct payments to employer-sponsored retirement plans
- Recharacterized IRA contributions
- Roth IRA conversions, and
- Premiums paid by a trustee or custodian for the cost of life insurance protection
- Distributions to plan participants from governmental Section 457(b) deferred compensation plans
Savings bonds
For redeemed United States savings bonds, Box 1 will contain the value of bonds distributed from a plan. The taxable amount of redeemed bonds should appear in Box 2a.
You should also receive a statement indicating the value of each bond at the time of distribution. This should give you the necessary information to calculate interest income for each redeemed bond.
Health insurance premiums
Box 1 may also contain amounts distributed from a qualified retirement plan:
- For which you choose to pay health insurance premiums under a cafeteria plan, or
- Paid directly to reimburse medical care expenses
This amount should also appear in Box 2a.
You may also see payments for qualified long-term care insurance contracts under combined arrangements in Box 1.
Death benefits
Death benefits should appear in Box 1. However, you should not see accelerated death benefits here. You should see accelerated death benefits on IRS Form 1099-LTC.
Section 1035 exchanges
For IRC Section 1035 exchanges that are reportable on the Form 1099-R tax form, you should see the information reported as follows:
- Box 1: Total value of the contract
- Box 2a: $0
- Box 5: Total premiums paid
- Box 7: Code 6
Designated Roth account distributions
If you received a distribution from a designated Roth account during the tax year, you should see the following information reported:
- Box 1: Gross distribution
- Box 2a: Taxable portion of the distribution
- Box 5: Basis included in the distributed amount
- Box 10: Any amount allocable to an in-plan Roth rollover (IRR)
- Box 11: First year of the 5-year tax period for determining qualified distributions
Your custodian should also enter the applicable code(s) in Box 7.
Employer securities and other property
If you received employer securities or other property, your employer should include the fair market value in Box 1. If you received worthless property, your employer may not file Form 1099-R.
Box 2a: Taxable amount
In general, you’ll see the taxable amount of any distribution from Box 1 in Box 2a.
However, the payer may leave this box blank if they cannot ascertain any additional information about whether there was a taxable distribution.
You should see ‘0’ in Box 2a for any of the following types of transactions:
- A direct rollover (other than an IRR) to a traditional IRA or a similar plan from:
- A qualified plan,
- A section 403(b) plan, or
- A governmental section 457(b) plan
- A direct rollover from a designated Roth account to a Roth IRA
- An amount from a traditional, SEP, or SIMPLE IRA directly transferred to an accepting employer plan;
- An IRA recharacterization;
- A nontaxable Section 1035 exchange of contracts for:
- Life insurance
- Annuity
- Endowment, or
- Long-term care insurance; or
- A nontaxable charge or payment, for the purchase of a qualified long-term care insurance contract, against the cash value of an annuity contract or the cash surrender value of a life insurance contract.
Box 2b
Taxable amount not determined: If the payer cannot reasonably ascertain the taxable distribution amount, then the payer will check this box.
Total distribution: If the reported transaction resulted in a complete distribution of the account balance, the payer will check this box.
If there were periodic or installment payments, then the payer will mark this box in the year of the final payment.
Box 3: Capital gain
If any amount of the distribution is a capital gain, then Box 3 will contain the amount of capital gain.
Box 4: Federal income tax withheld
You should see any federal taxes withheld in Box 4.
IRS Publication 15-A and IRS Form 945 Instructions may contain additional information about withholding guidelines.
See Pub. 15-A, Employer’s Supplemental Tax Guide, and the Instructions for Form 945 for more withholding information.
Eligible rollover distributions
If the account custodian is paying the eligible rollover distribution directly to an eligible retirement plan in a direct rollover, then the account custodian should not withhold federal income tax.
However, if any part of an eligible rollover distribution is not a direct rollover, then the account custodian or plan administrators must withhold 20% of the distribution amount. This includes the earnings portion of any nonqualified designated Roth account distribution that is not a direct rollover.
The recipient cannot claim exemption from the 20% withholding. However the recipient may ask to have additional amounts withheld on IRS Form W-4P, Withholding Certificate for Pension or Annuity Payments.
IRAs
The 20% withholding does not apply to IRA distributions. However, withholding does apply to IRAs under the rules for periodic payments and nonperiodic distributions. An IRA recharacterization is not subject to income tax withholding.
Box 5: Employee contributions/Designated Roth contributions or insurance premiums
Box 5 should contain any of the following:
- Employee contributions
- Designated Roth contributions
- Insurance premiums that you may recover tax free
- Even if they exceed the Box 1 amount
This may also include:
- Designated Roth contributions made on your behalf under the plan that were required to be included in your taxable income (after-tax contributions)
- Employer contributions that are considered to have been made by you under IRC Section 72(f)
- Accumulated cost of premiums paid for life insurance protection taxable to you in previous years and in the current calendar year, and
- Premiums paid on commercial annuities
This box should not contain any elective deferrals or any pre-tax retirement plan contributions.
If periodic payments began before 1993, you may see, but not always, a Box 5 entry.
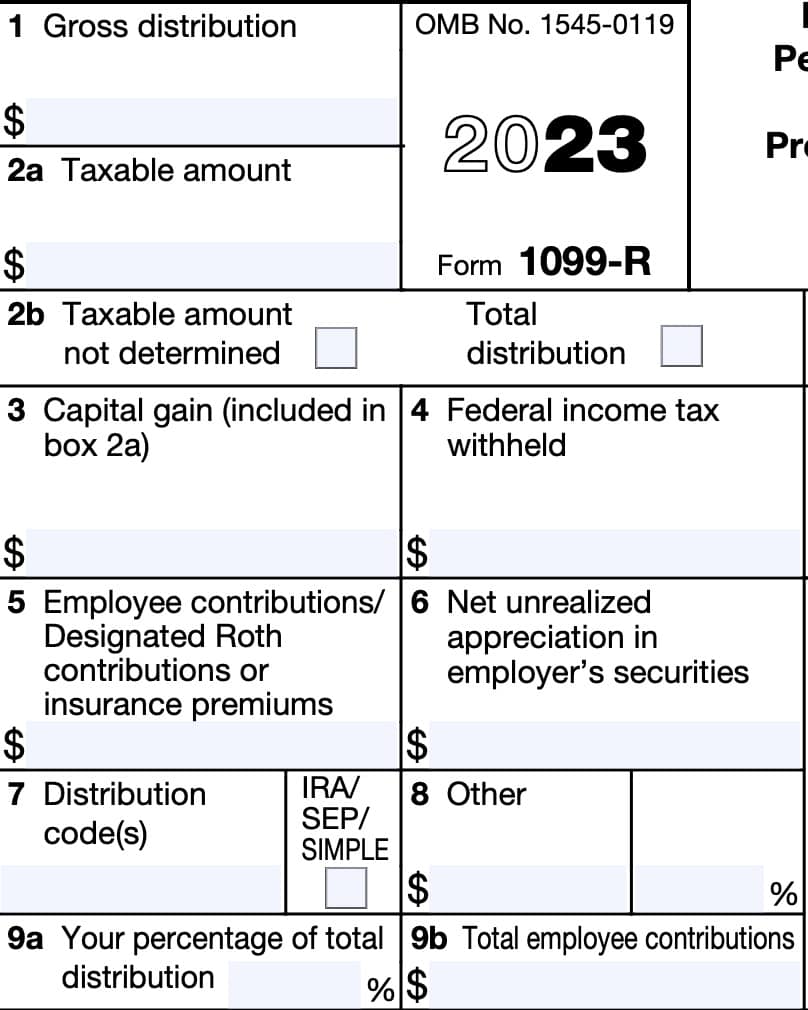
Box 6: Net unrealized appreciation in employer’s securities
If you participate in an employer-sponsored plan that contains employer’s securities, you may see an entry in Box 6 if:
- A distribution from a qualified plan includes securities from the employer, and
- Except a qualified distribution from a Roth account
- The plan administrators can compute the net unrealized appreciation (NUA) in those securities
If this is a lump-sum distribution, then you should see all of the NUA in this box. Otherwise, Box 6 will only contain the NUA in employer securities that are attributable to your employee contributions.
Box 7: Distribution code
If the distribution is from a traditional IRA, SEP IRA, or SIMPLE IRA, then you should see an ‘X’ in the IRA/SEP/SIMPLE box. You should not see this box checked for a distribution from a Roth IRA or for an IRA recharacterization.
Otherwise, you should see one or two distribution codes entered in Box 7. Only three numeric combinations are permitted on one Form 1099-R:
- Codes 8 & 1
- Codes 8 & 2
- Codes 8 & 4
If two or more other numeric codes are applicable, you may see more than one Form 1099-R.
For example, if part of a distribution is premature (Code 1) and part is not (Code 7), then you’ll see one Form 1099-R for the part to which Code 1 applies and another Form 1099-R for the part to which Code 7 applies.
Below is a list of distribution codes and their meanings.
Distribution code 1: Early distribution; no known exception
Explanation: The payer will use Code 1 only if you have not reached age 59½, and if they do not know whether any of the exceptions under Code 2, 3, or 4 apply.
However, Code 1 will be used even if the distribution is made for any of the following:
- Medical expenses
- Health insurance premiums
- Qualified higher education expenses
- First-time home purchase
- Qualified reservist distribution, or
- Qualified birth or adoption distribution
Code 1 must also be used even if a taxpayer is 59½ or older and he or she modifies a series of substantially equal periodic payments under IRC Section 72(q), (t), or (v) prior to the end of the 5-year period which began with the first payment.
Can be used with code(s): 8, B, D, K, L, M, or P
Distribution code 2: Early distribution; exception applies
Explanation: The payer will use distribution code 2 if this is an early distribution, but a known exception applies:
- Roth IRA conversion (an IRA converted to a Roth IRA).
- Distribution made from a qualified retirement plan or IRA because of an IRS levy under IRC Section 6331.
- A governmental Section 457(b) plan distribution that is not subject to the
additional 10% tax. - A distribution from a qualified retirement plan after separation from service in or after the year the participant has reached age 55.
- A distribution from a governmental defined benefit plan to a public safety employee after separation from service, in or after the year the employee has reached age 50.
- A distribution that is part of a series of substantially equal periodic payments, as described in IRC Section 72(q), (t), (u), or (v).
- A distribution that is a permissible withdrawal under an eligible automatic contribution arrangement (EACA).
- Any other distribution subject to an exception under IRC Section 72(q), (t), (u), or (v) that is not required to be reported using Code 1, 3, or 4.
Can be used with code(s): 8, B, D, K, L, M, or P
Distribution code 3: Disability
Explanation: For additional information, see IRC Section 72(m)(7).
Can be used with code(s): D
Distribution code 4: Death
Explanation: The payer will use distribution code 4 regardless of the age of the participant to indicate payment to a decedent’s beneficiary, including an estate or trust.
Also, the payer may use it for death benefit payments made by an employer but not made as part of a pension, profit-sharing, or retirement plan, or for payments of reportable death benefits.
Can be used with code(s): 8, A, B, D, G, H, K, L, M, or P
Distribution code 5: Prohibited transaction
Explanation: Code 5 reports a prohibited transaction within an IRA and means the account is no longer an IRA.
Can be used with code(s): None
Distribution code 6: Section 1035 exchange
Explanation: Code 6 indicates the tax-free exchange of the following contracts under IRC Section 1035:
- Life insurance
- Annuity
- Long-term care insurance
- Endowment contracts
Can be used with code(s): W
Distribution code 7: Normal distribution
Explanation: Code 7 indicates a normal distribution from the account. This can include any of the following:
- Normal distribution from a qualified plan or traditional IRA, if the employee or taxpayer is at least 59½;
- Roth conversion if the participant is at least 59½;
- Distribution from a life insurance, annuity, or endowment contract, and to report income from a failed life insurance contract
Generally, the payer will indicate Code 7 if no other code applies. However, you should not see this code for a Roth IRA distribution.
Can be used with code(s): A, B, D, K, L, or M
Distribution code 8: Excess contributions plus earnings/excess deferrals (and/or earnings) taxable in the current year
Explanation: You may see Code 8 for an IRA distribution under IRC Section 408(d)(4), unless Code P applies. Also, you may see this code for any of the following unless Code P applies:
- Corrective distributions of excess deferrals
- Excess contributions
- Excess aggregate contributions
Can be used with code(s): 1, 2, 4, B, J, or K
Distribution code 9: Cost of current life insurance protection
Explanation: Code 9 reports premiums paid by a trustee or custodian for current life or other insurance protection.
Can be used with code(s): None
Distribution code A: May be eligible for 10-year tax option
Explanation: Payers will enter Code A only for:
- Plan participants born before January 2, 1936, or
- Beneficiaries of plan participants born before January 2, 1936
This indicates that the distribution may be eligible for the 10-year tax option method of computing the tax on lump-sum distributions. Taxpayers may select this option by filing IRS Form 4972, Tax on Lump-Sum Distributions.
Can be used with code(s): 4 or 7
Distribution code B: Designated Roth account distribution
Explanation: Code B indicates a distribution from a designated Roth account.
Can be used with code(s): 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, G, L, M, P, or U
Distribution code C: Reportable death benefits under section 6050Y
Explanation: Payers will use Code C to report payments of reportable death benefits.
Can be used with code(s): D
Distribution code D: Annuity payments from nonqualified annuities and distributions from life insurance contracts that may be subject to tax
Explanation: Indicates a distribution from any plan or arrangement not described in:
- Section 401(a)
- Section 403(a)
- Section 403(b)
- Section 408
- Section 408A
- Section 457(b)
Can be used with code(s): 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, or C
Distribution code E: Distributions under Employee Plans Compliance Resolution System (EPCRS)
Explanation: Code E indicates a Section 415 distribution under EPCRS
Can be used with code(s): None
Distribution code F: Charitable gift annuity
Explanation: If cash or capital gain property is donated in exchange for a charitable gift annuity, then annuity distributions will be reported on Form 1099-R with Code F.
Can be used with code(s): None
Distribution code G: Direct rollover and direct payment
Explanation: Code G indicates a direct rollover to an eligible retirement plan from:
- Qualified plans
- Section 403(b) plans, or
- Governmental Section 457(b) plans
Also, Code G can indicate a direct payment from an IRA to an accepting employer plan, and for IRRs that are direct rollovers.
Can be used with code(s): 4, B, or K
Distribution code H: Direct rollover of a designated Roth account distribution to a Roth IRA.
Explanation: Code H means a direct rollover of a distribution from a designated Roth account to a Roth IRA.
Can be used with code(s): 4
Distribution code J: Early distribution from a Roth IRA
Explanation: Code J indicates an early distribution from a Roth IRA when Code Q (qualified distribution) or Code T (applicable exception) do not apply.
Can be used with code(s): 8, P
Distribution code K: Distribution of traditional IRA assets not having a readily available FMV
Explanation: Code K can indicate distributions of IRA assets that do not have a readily available fair market value (FMV). These assets can include:
- Stock, other ownership interest in a corporation, short- or long-term debt obligations, not readily tradable on an established securities market;
- Ownership interest in a limited liability company (LLC), partnership, trust, or similar entity (unless the interest is traded on an established securities market);
- Real estate;
- Option contracts or similar products not offered for trade on an established option exchange; or
- Other asset that does not have a readily available FMV.
Can be used with code(s): 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, or G
Distribution code L: Loans Treated as Deemed Distributions under Section 72(p)
Explanation: If a loan is treated as a deemed distribution, it is reportable on Form 1099-R using the normal taxation rules of IRC Section 72, including tax basis rules.
Can be used with code(s): 1, 2, 4, 7, or B
Distribution code M: Qualified plan loan offset
Explanation: Code M stands for a qualified plan loan offset. This generally is a type of plan loan offset due to severance from employment or termination of the plan.
Can be used with code(s): 1, 2, 4, 7, or B
Distribution code N: Recharacterized IRA contribution
Explanation: This code indicates a recharacterization of an IRA contribution made for the current tax year, and and recharacterized in the same tax year to another type of IRA by a trustee-to-trustee transfer or with the same trustee.
Can be used with code(s): None
Distribution code P: Excess contributions plus earnings/excess deferrals taxable in previous tax year
Explanation: The IRS suggests that anyone using Code P for the refund of an IRA contribution under IRC Section 408(d)(4), including excess Roth IRA contributions, advise payees, at the time the distribution is made, that the earnings are taxable in the year in which the contributions were made.
Can be used with code(s): 1, 2, 4, B, or J
Distribution code Q: Qualified distribution from a Roth IRA
Explanation: Code Q indicates a distribution from a Roth IRA in which the participant meets the 5-year holding period and:
- The participant has reached age 59½,
- The participant died, or
- The participant is disabled.
Can be used with code(s): None
Distribution code R: Recharacterized IRA contribution made for prior tax year
Explanation: Code R for a recharacterization of an IRA contribution made for the previous tax year and recharacterized in the current tax year to another type of IRA by a trustee-to-trustee transfer or with the same trustee.
Can be used with code(s): None
Distribution code S: Early distribution from a SIMPLE IRA in the first 2 years, no known exception.
Explanation: Code S can be used only if the distribution is
- From a SIMPLE IRA in the first 2 years,
- Employee or taxpayer has not reached age 59½, and
- None of the IRC Section 72(t) exceptions apply
The 2-year period begins on the day contributions are first deposited in the individual’s SIMPLE IRA. If Code 3 or 4 applies, then you should not see Code S.
Can be used with code(s): None
Distribution code T: Roth IRA distribution, exception applies
Explanation: Code T stands for a distribution from a Roth IRA if the account custodian does not know if the 5-year holding period has been met but:
- The participant has reached age 59½,
- The participant died, or
- The participant is disabled.
Can be used with code(s): None
Distribution code U: Dividends Distributed from an ESOP under Section 404(k)
Explanation: Code U indicates a distribution of dividends from an employee stock ownership plan (ESOP) under section 404(k). These are not eligible rollover distributions.
Can be used with code(s): B
Distribution code W: Charges or payments for purchasing qualified long-term care insurance contracts under combined arrangements
Explanation: Code W is used for charges or payments for purchasing qualified long-term care insurance contracts under combined arrangements which are excludable under section 72(e)(11) against the cash value of an annuity contract or the cash surrender value of a life insurance contract.
Can be used with code(s): 6
Box 8: Other
Box 8 may contain current actuarial value of an annuity contract that is part of a lump-sum distribution. This item will not appear in Boxes 1 and 2a.
This value should equal the actuarial value of the annuity contract, reduced by any amount equal to the excess of your contributions over the distribution amount.
If an annuity contract is part of a multiple recipient lump-sum distribution, Box 8 should contain, along with the current actuarial value, the percentage of the total annuity contract each Form 1099-R represents.
Box 8 should also contain the amount of the reduction in the investment against the cash value of an annuity contract or the cash surrender value of a life insurance contract due to charges or payments for qualified long-term care insurance contracts. However, this amount cannot be below zero.
Box 9a: Your percentage of total distribution
If this is a total distribution and it is made to more than one person, Box 9a should contain the amount that you received. However, the custodian may not complete Box 9a for any IRA distributions or for a direct rollover.
Box 9b: Total employee contributions
This is an optional field, as your employer does not have to enter the total employee contributions or designated Roth contributions in Box 9b.
This will not include any amounts recovered tax free in prior years.
Boxes 10 through 13
On the bottom left side of the form sit Boxes 10 through 13. Let’s go through each of them.
Box 10: Amount allocable to IRR within 5 years
Box 10 will contain the amount of the distribution allocable to an IRR made within the 5-year period beginning with the first day of the year in which the rollover was made.
However, if a Section 72(t) exception applies, this box may be empty.
Box 11: First year of designated Roth contribution
Box 11 should contain the first year of the 5-tax-year period. This is the year in which you first established the designated Roth account.
Box 12: FATCA filing requirement
A foreign financial institution (FFI) may check Box 12 if reporting a cash value insurance contract or annuity contract as required under IRC Section 6047(d). Also, a U.S. payer may check this box as part of satisfying Chapter 4 reporting requirements, outlined in Treasury Regulations Section 1.1471-4(d)(2)(iii)(A).
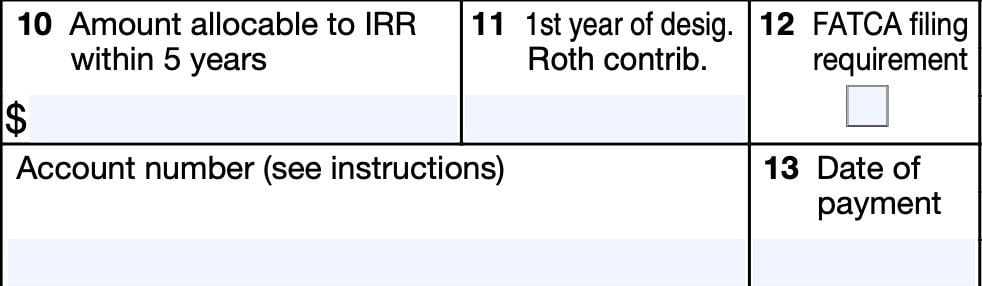
Account number
If applicable, your account custodian or plan administrator may enter an account number in this field.
Box 13: Date of payment
Box 13 will contain the date that payment was made for reportable death benefits under IRC Section 6050Y.
Boxes 14 through 19
Boxes 14 through 19 may be optional fields if you live in a state or locality without tax consequences. There is no IRS requirement for any information to be entered in boxes 14 through 19.
Box 14: State tax withheld
If applicable, Box 14 should contain any state tax withholdings.
Box 15: State/Payer’s state number
The abbreviated name of the state and the payer’s state identification number should appear in Box 15.
Box 16: State distribution
If applicable, this box contains the distribution amount subject to state taxes.

Box 17: Local tax withheld
If applicable, Box 17 should contain any tax withholdings for local tax purposes.
Box 18: Name of locality
If needed, Box 18 should contain the name of the appropriate local government.
Box 19: Local distribution
If applicable, Box 19 contains the distribution amount subject to local taxes.
Filing IRS Form 1099-R
For tax entities who must file this tax form with the Internal Revenue Service, the IRS requires certain paper versions of information returns to be accompanied by IRS Form 1096, Annual Summary and Transmittal of U.S. Information Returns.
Check out our step-by step instructional guide for more information on how to submit your information return with IRS Form 1096.
Video walkthrough
Watch this informative video for step by step guidance on how to get tax information from your Form 1099-R!
Do you use TurboTax?
If you don’t, is it because the choices are overwhelming to you?
If so, you should check out our TurboTax review page, where we discuss each TurboTax software product in depth. That way, you can make an informed decision on which TurboTax offering is the best one for you!
Click here to learn more about which TurboTax option is best for you!
Frequently asked questions
The Internal Revenue Service requires payers and financial institutions to make Forms 1099-R available to recipients by January 31 of the following tax year.
Some employers and financial institutions allow payees to choose to receive their tax forms online. If you have selected this option, you may receive your Form 1099-R online.
Box 1 should contain the entire transaction amount. The taxable distribution should be reported on Box 2a.
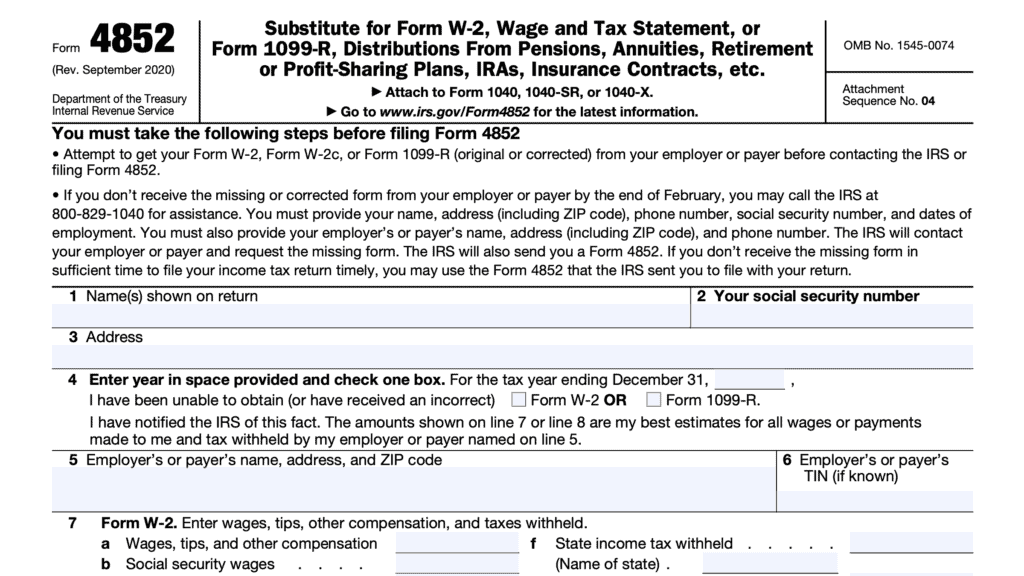
If you have not received this form by February 14, you should ask the IRS for assistance. The IRS will contact the employer/payer on your behalf. If you still do not receive the form, you may need to complete IRS Form 4852 as a substitute statement.
Where can I find IRS Form 1099-R?
As with other IRS tax forms, you can find IRS Form 1099-R on the IRS website. For your convenience, we’ve enclosed an example of what Form 1099-R looks like, right here.
Related tax articles
This tax form is one of the fillable tax forms provided by the Internal Revenue Service, to help taxpayers reduce their tax preparation costs. To see more forms like this, visit our free fillable tax forms page, where you’ll also find articles like this.
Unlike the IRS, our articles contain step by step instructions for each tax form, as well as video walkthroughs. You can also check out all of our videos by subscribing to our YouTube channel!