IRS Form 56 Instructions
A fiduciary relationship is crucial in situations where the primary taxpayer is unable to handle his or her own financial or tax matters. The fiduciary duty is also important in cases where a government authority must grant permission for assets to be distributed, such as in bankruptcy proceedings or execution of a decedent’s estate. Taxpayers use IRS Form 56 to notify the IRS of situations where fiduciary responsibility is granted to another person or entity.
This article will walk you through this tax form, including:
- When you should use Form 56
- When other tax forms are more appropriate
- How to complete and file IRS Form 56
Let’s start with step by step instructions on how to complete IRS Form 56.
Table of contents
How do I complete IRS Form 56?
There are 4 parts to this two-page tax form which we’ll walk through step by step:
- Part I: Identification
- Part II: Revocation or Termination of Notice
- Part III: Court and Administrative Proceedings
- Part IV: Signature
Let’s start with Part I.
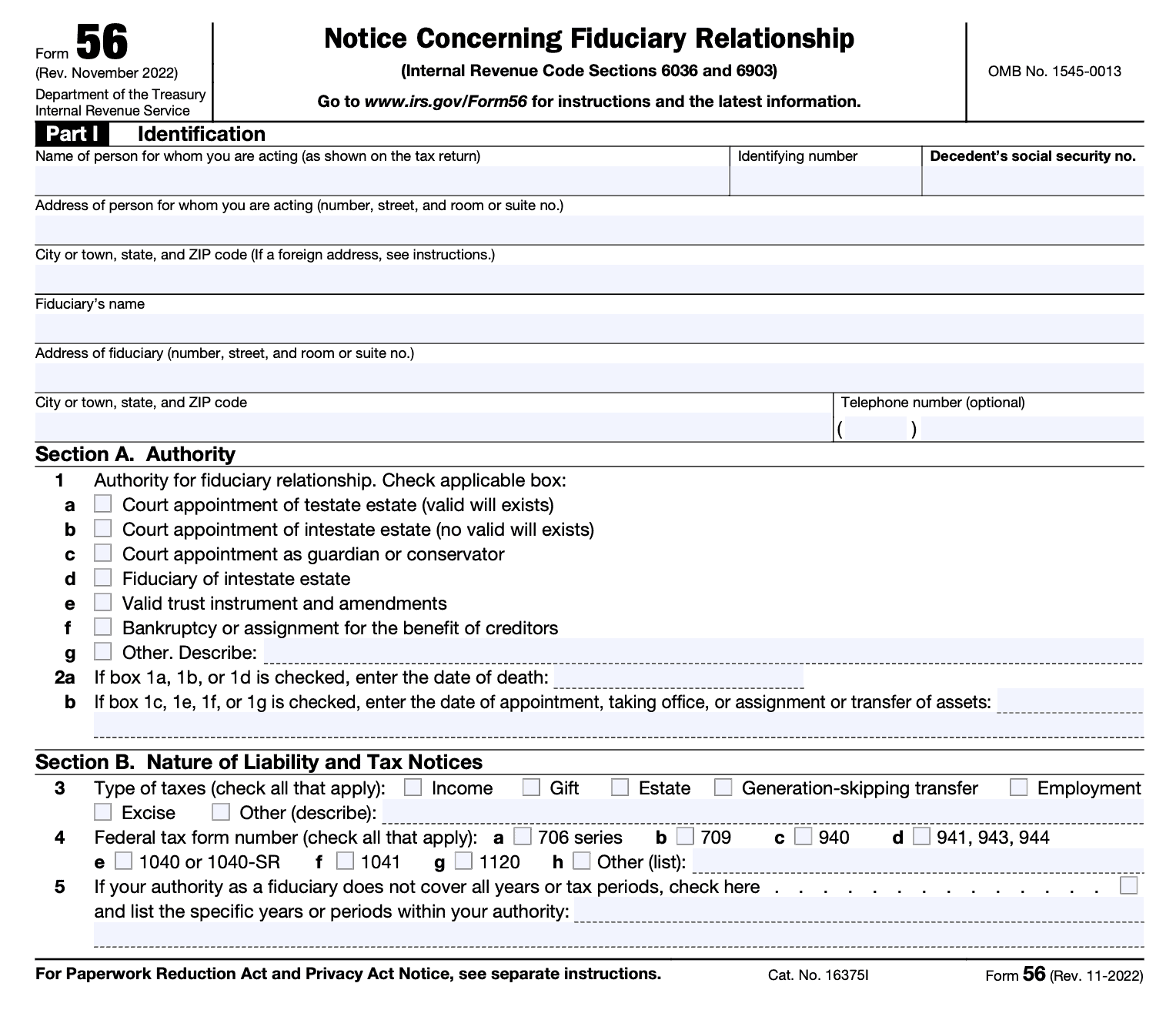
Part I: Identification
Aside from the identification fields at the top, there are also two sections to Part I:
- Section A: Authority
- Section B: Nature of Liability and Tax Notices
Let’s start with the identifying information.
Identifying information
In this field, you’ll enter all applicable information about the taxpayer and the person assuming the fiduciary duty. This includes:
- Taxpayer’s name and identifying number
- You must file a separate Form 56 for each taxpayer
- If filing a decedent’s final tax return and you are the executor of the decedent’s estate, you must file a separate form for the decedent and the decedent’s estate
- Decedent’s Social Security number, if applicable
- Street address, including city, state, and zip code
- If the address is a P.O. Box, use this only if the post office does not deliver mail to the street address
- If the address is a foreign address, list city/town, province/state, and country. Do not abbreviate the country’s name
Section A: Authority
Check the appropriate box. Below are some key points:
Testate estate
This means that a valid will exists, and an appropriate court has authorized you to perform as a representative of the decedent’s estate. Attach current letters testamentary or a court certificate as proof of your court appointment.
List the decedent’s date of death in Line 2a.
Intestate estate
The decedent passed away without a valid will in place. Attach current letters testamentary or a court certificate as proof of your court appointment.
List the decedent’s date of death in Line 2a.
Guardianship or conservator
Check this box if if a court of appropriate jurisdiction has appointed you to serve over another person or entity as one of the following:
- Guardian
- Custodian
- Conservator
Enter the date of your appointment in Box 2b.
Fiduciary of intestate estate
Only check this box if:
- There is no court appointed administrator or representative for the decedent’s estate, and
- You are the sole person charged with the property of the decedent.
List the decedent’s date of death in Line 2a.
Valid trust instrument and amendments
Use this if you have been appointed as a trustee in a trust document.
Enter the date of your appointment in Box 2b.
Bankruptcy
Use this field if you are a bankruptcy trustee or assignee for the benefit of creditors.
Enter the date of your appointment in Box 2b.
Other
Describe the authority for the fiduciary relationship in the space provided.
Also, enter the date of your appointment in Box 2b.
Section B: Nature of Liability and Tax Notices
Use these fields to describe the following:
- Type of taxes that are part of your fiduciary responsibility (Line 3)
- Type of tax forms you expect to file in your fiduciary duty (Line 4)
- Specific tax years or periods within your authority (Line 5)
- If your fiduciary duty covers all tax periods, leave the box unchecked and the lines blank
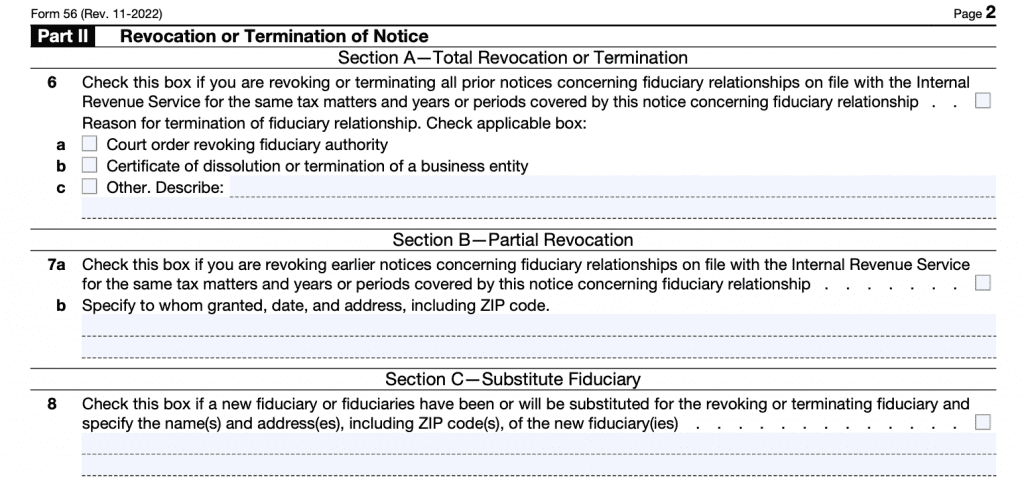
Part II: Revocation or Termination of Notice
Only complete Part II if revoking or terminating prior notices. Completing Section B or C does not relieve any new or substitute fiduciary of the requirement to give the IRS proper notice.
Section A: Total revocation or termination
Check this box to completely revoke or terminate all prior notices regarding fiduciary relationships. Also check the appropriate box for termination.
Section B: Partial revocation
Use this to revoke earlier notices, but would like to specify the tax matters, tax years, or tax periods that you wish to revoke.
Section C: Substitute fiduciary
Check this box if a new fiduciary or fiduciaries have been or will be substituted. Specify the name(s) and address(es) of the new fiduciary or fiduciaries.
Even after you select this option, new fiduciaries still must have a Form 56 on file with the IRS.
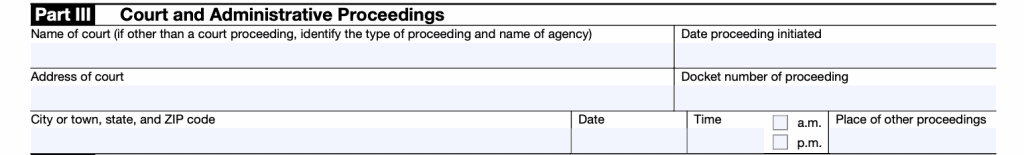
Part III: Court and Administrative Proceedings
Only complete this part if you have been appointed a receiver, trustee, or fiduciary by a court or other governmental unit in a proceeding besides a bankruptcy proceeding.
Enter the following information:
- Name of court or agency and type of proceeding
- Date of proceeding
- Address of court or proceeding location
- Docket number
- Date and time of proceedings
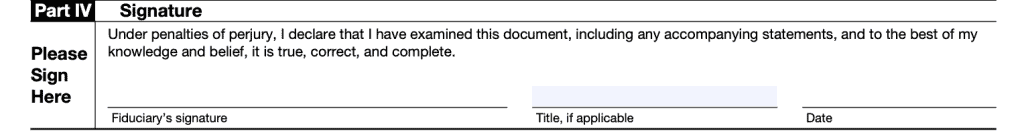
Part IV: Signature
Part IV contains your signature, sworn under penalties of perjury, that this document is true, correct, and complete to the best of your knowledge.
What is IRS Form 56?
IRS Form 56, Notice Concerning Fiduciary Relationship, is the tax form that provides the Internal Revenue Service:
- Proper notification of the creation or termination of a fiduciary relationship under Internal Revenue Code (IRC) Section 6903
- Notice of qualification as executor or receive as required in IRC Section 6036
Which begs the question, “What is a fiduciary relationship?”
Examples of fiduciary relationships
The IRS website cites the following examples of fiduciaries:
- Administrators
- Conservators
- Designees
- Executors
- Guardians
- Receivers
- Trustees of a trust
- Trustees in bankruptcy proceedings
- Personal representatives
- Persons in possession of property of a decedent’s estate, or
- Debtors-in-possession of assets in any bankruptcy proceeding by order of the court
Difference between fiduciary and representative
Taxpayers must inform the IRS of the creation of a fiduciary relationship for a very important reason:
A fiduciary has much broader authority to perform duties on behalf of the taxpayer than someone who is simply an authorized representative of the taxpayer.
The IRS treats someone acting in a fiduciary capacity as if he or she were the actual taxpayer, not merely a personal representative or someone with power of attorney privileges. This means that the fiduciary has the rights and responsibilities (such as filing proper tax returns and paying taxes owed) of the actual taxpayer.
Conversely, an appointed representative may only have duties as specifically authorized by the taxpayer. A representative is not allowed to perform any function that the taxpayer has not explicitly authorized.
When do I NOT file IRS Form 56?
The IRS form instructions state that Form 56 is erroneously used in tax matters where different tax forms are more appropriate. Below are some of the more common examples when you should not file Form 56:
Do not use IRS Form 56 when updating an address
Instead, you should use one of the following IRS forms:
- IRS Form 8822: Change of Address
- IRS Form 8822-B: Change of Address, Responsible Party-Business
Using one of these forms is the proper way to notify the IRS of a change in address of the person listed on the tax form.
Do not use IRS Form 56 if you are an authorized representative of the taxpayer
Instead, you should file IRS Form 2848, Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative. This form grants powers to represent the taxpayer in administrative matters before the IRS. However, the IRS does not treat the representative on Form 2848 as if he or she were the taxpayer.
By using Form 2848, the taxpayer can still dictate which duties their representative is authorized to perform.
Video walkthrough
Watch this instructional video to learn more about how to notify the IRS of your fiduciary relationship.
Do you use TurboTax?
If you don’t, is it because the choices are overwhelming to you?
If so, you should check out our TurboTax review page, where we discuss each TurboTax software product in depth. That way, you can make an informed decision on which TurboTax offering is the best one for you!
Click here to learn more about which TurboTax option is best for you!
Frequently asked questions
You should file this form with the Internal Revenue Service center or the IRS department who normally has jurisdiction over the taxpayer’s tax issues.
According to the IRS, a fiduciary is any person in a position of confidence acting on behalf of any other person. A fiduciary assumes the powers, rights, duties, and privileges of the person or entity on whose behalf he or she is acting.
The IRS treats someone acting in a fiduciary capacity as if he or she were the actual taxpayer, not merely a personal representative or someone with power of attorney privileges. This means that the fiduciary has the rights and responsibilities (such as filing proper tax returns and paying taxes owed) of the actual taxpayer. Conversely, an appointed representative may only have duties as specifically authorized by the taxpayer. A representative is not allowed to perform any function that the taxpayer has not explicitly authorized.
Generally, the IRS recommends filing Form 56 when creating or terminating a fiduciary relationship. Specifically, receivers in receivership hearings or assignees for the benefit of creditors, should file Form 56 within 10 days of meeting with the Advisory Group Manager for the IRS center with jurisdiction over the taxpayer.
Where can I find IRS Form 56?
You can find this form on the IRS website. For your convenience, the most current version is available for download at the end of this article.