IRS Form 730 Instructions
If you are in the business of accepting gambling wagers, the Internal Revenue Service may require you to report them on a monthly basis using IRS Form 730. In this article, we’ll help you understand everything you need to know about IRS Form 730, including:
- How to complete and file IRS Form 730
- What type of gambling activities Form 730 covers
- Other filing considerations
Let’s begin by going through this tax form.
Table of contents
How do I complete IRS Form 730?
Let’s take a closer look at this one-page tax form, starting with the taxpayer information fields at the top.
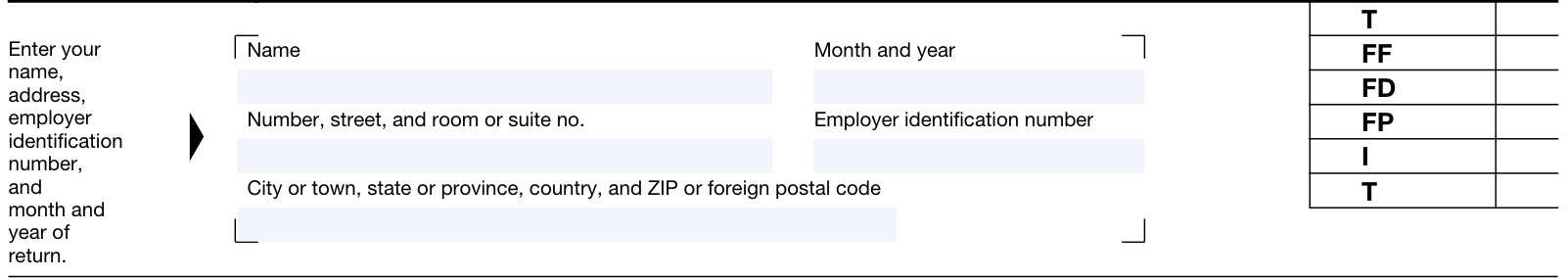
Taxpayer information
Enter taxpayer information as indicated at the top of the form, beginning with the taxpayer name.
Taxpayer name
Enter the name shown on the eligible entity’s most recently filed federal income tax return.
Month and year
Enter the month and year for the date of the tax return in MM/YYYY format. For example, if you are reporting wagers accepted during April 2024, then you would enter 04/2024.
Taxpayer address
Include the suite, room, or other unit number after the street address.
If the Post Office doesn’t deliver mail to the street address and the entity has a P.O. box, show the box number instead of the street address.
Foreign address
When entering the address for an entity located in a foreign country, follow the country’s practice for entering the postal code.
In some countries the postal code may come before the city or town name. Enter the full name of the country using uppercase letters in English.
Employer identification number
Enter the taxpayer’s employer identification number (EIN) as shown on the most recent tax return. If you do not have an EIN, you may request one from through the Internal Revenue Service website or by filing IRS Form SS-4.
Lines 1 through 6
This is the main part of your monthly tax return. Before we go to Line 1, be sure to check the boxes marked final return and address change as applicable.
Final return
If you stop accepting wagers, check the final return box here.
Address change
If you are reporting a change in address, check this box.
According to Revenue Procedure 2010-16, you do not need to file IRS Form 8822-B, Change of Address or Responsible Party, Business, if you report a change of address while filing the required tax return.
Line 1
Enter the gross amount of wagers accepted during the month, not including laid-off wagers.
Laid-off wagers
A layoff bet is a bet that bookmakers may place with another activity to protect against excess losses and to equalize the total amount of money on either side of the wager.
Enter such wagers in Line 2, below.
Line 2
Enter the gross amount of laid-off wagers accepted during the month.
The gross laid-off amount is the total of laid-off wagers that are authorized and those wagers not authorized by the state in which they are accepted.
Line 3
Add Line 1 and Line 2. Enter the total in Line 3.
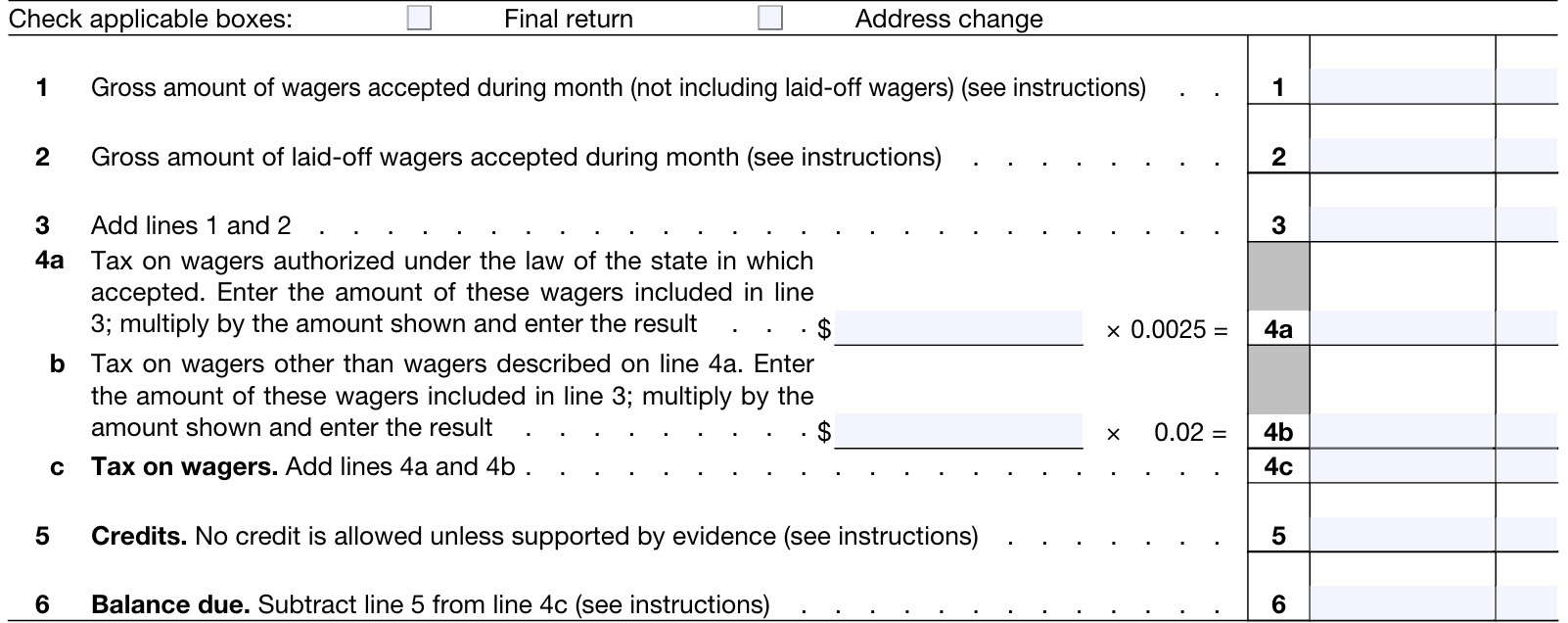
Line 4a
In Line 4a, calculate the tax on wagers authorized under the law of the state in which the wagers were accepted.
Determine this from the Line 3 amount, and enter such wagers in the space provided. Multiply by the tax rate in Line 4a, (currently 0.25%), then enter the result in Line 4a.
Line 4b
In Line 4b, calculate the tax on wagers not authorized under the law of the state in which the wagers were accepted.
Determine this from the Line 3 amount, and enter such wagers in the space provided. Multiply by the tax rate in Line 4b, (currently 2.0%), then enter the result in Line 4b.
Line 4c: Tax on wagers
Add Line 4a and Line 4b, then enter the total in Line 4c.
Line 5: Credits
Enter the amount of tax credits in Line 5.
You may be able to claim a credit for the amount of:
- Any overpayment of tax, or
- Tax imposed with respect to a wager that you laid off.
You may also claim a tax credit by filing IRS Form 8849, Claim for Refund of Excise Taxes, using Schedule 6 (Form 8849), Other Claims, to make a claim for refund.
Credit for overpayment of tax
As a general rule, you may claim a credit for any overpayment of tax. You must file your claim within the later of the following:
- 3 years from the time the Form 730 reporting the tax was filed, or
- 2 years from the time the tax was paid
The IRS will not allow any tax credit regarding the tax overpayment unless you attach a written statement with the following detailed information:
- Explanation of the reason for claiming a tax credit
- Date of payment and tax amount
- Whether any previous claim has been filed covering any part of the amount involved
- Statement that you:
- Have not collected the amount of tax from the person that placed the wager on which the tax is imposed, or
- Have repaid the amount of tax to the person that placed the wager, or
- Have the written consent of the person who placed the wager
- You must attach the written consent to the tax return
If the overpayment relates to a laid-off wager that you accepted, one of the three statements in the previous bullet must be attached for both of the following individuals
- The person who placed the laid-off wager with you, and
- The person who placed the original wager
Credit for tax imposed with respect to a wager you laid off
If you accept a wager and lay off all or a part of that wager with a person who is liable for tax, then you’ll need to follow the rules below to claim a credit depending on whether or not you paid the tax.
If you haven’t paid the tax yet
You may claim a credit on Form 730 in the amount of the tax due for the laid-off wager, if the certificate described in Treasury Regulations Section 44.6419-2(d) is attached to Form 730 for the month during which the wager was accepted and laid off.
If you have paid the tax
If you have paid the tax, you may claim a tax credit for the tax paid on the laid-off amount.
The claim must be filed within 3 years from the time the return reporting the tax was filed or 2 years from the time the tax was paid, whichever is later.
Interest is not allowed on a credit for the tax imposed on a wager that you laid off.
The IRS will not allow any credit unless you attach complete information to the return for each laid-off wager:
- The certificate described in Regulations Section 44.6419-2(d).
- A statement that includes the following:
- The reason for the tax credit
- The month in which the tax liability was paid
- The date of payment, and
- Whether any previous claim covering all or part of the amount involved has been filed.
Line 6: Balance due
Enter the amount of tax due.
If Line 4c is greater than Line 5, enter the difference on Line 6. You don’t have to pay if the Line 6 amount is under $1.00.
You may pay the amount shown on line 6 using the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS) or by check or money order.
If you pay using EFTPS, you don’t need to file IRS Form 730-V, Payment Voucher, mentioned below.
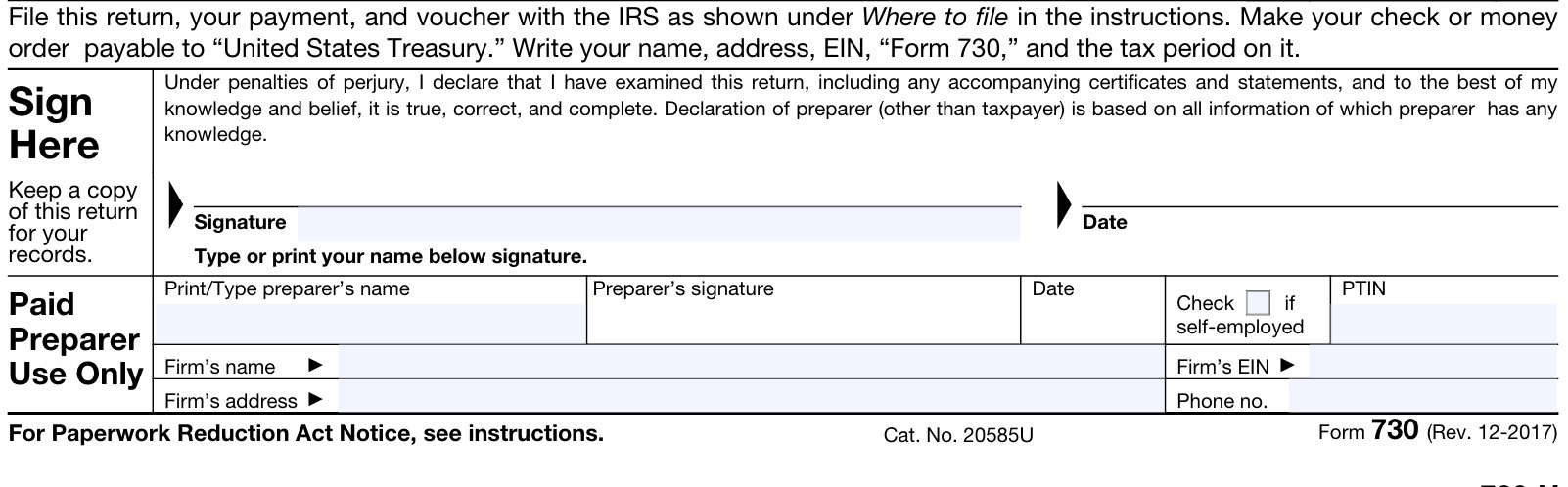
Taxpayer signature
Sign and date your completed Form 730 at the bottom of the form. If using a paid tax preparer, your tax professional will sign and date the form as well. In addition, your tax preparer will enter the following tax return information:
- Tax preparer name
- Preparer tax identification number (PTIN)
- Preparation firm’s name, address, and EIN
IRS Form 730-V, Payment Voucher
If you are making a payment by check or money order, you’ll need to use the payment voucher, IRS Form 730-V, included at the bottom of your Form 730.
Line 1: Employer identification number
Enter the taxpayer’s employer identification number in Line 1 of the tax voucher.
Line 2: Payment amount
In dollars and cents, enter the amount of the tax payment included with your voucher.
Payment instructions
According to the form instructions, you should do the following:
- Make your check or money order payable to: “United States Treasury”
- Write the following on your check or money order:
- Name
- Address
- EIN
- ‘Form 730’
- Tax period
- NOT staple or attach your payment voucher to your payment
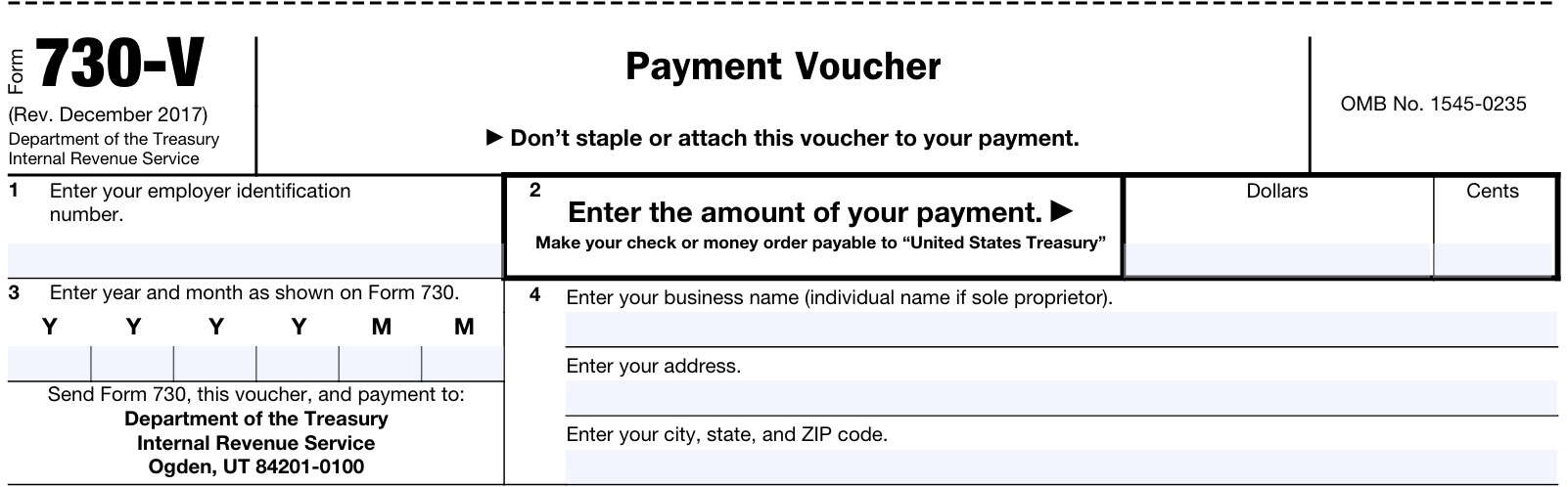
Line 3
Enter the year and month as shown on the Form 730 in YYYYMM format. For example, if reporting on taxable wagers placed in April 2024, you would enter, “202404.”
Line 4
Enter the following necessary information:
- Business name
- Business address, including city, state, and zip code
If you are a sole proprietor, you may enter your individual name.
Filing considerations
Below are some filing considerations based upon additional information in the form instructions.
Who must file IRS Form 730?
You must file Form 730 and pay the tax on wagers under Internal Revenue Code Section 4401(a) if you:
- Are in the business of accepting wagers,
- Conduct a wagering pool or lottery, or
- Must be registered and you received wagers for or on behalf of another person but you did not report that person’s name and address.
You may use IRS Form 11-C, Occupational Tax and Registration Return for Wagering, to register.
When must I file IRS Form 730?
If you’re liable for the tax on wagers, then you must file Form 730 for each month by the last day of the month following the month for which you’re reporting taxable wagers.
For example, if you are reporting wagers placed in April 2024, you must file Form 730 for the month of April by the last day of the following month, which is May 31, 2024.
The IRS won’t send you a legal notice that a return is due. You must file a return on a monthly basis whether or not you have taxable wagers to report.
If you have no tax to report, write “None” in the entry space for line 6 and sign and date Form 730. If you
stop accepting wagers, check the final return box above Line 1.
What is taxed?
According to the IRS, the tax applies only to wagers accepted in the United States or placed by a person who is in the United States with a person who is a U.S. citizen or resident.
Taxable wagers include those placed:
- On a sports event or contest with a person engaged in the business of accepting wagers on a sports event or contest;
- In a wagering pool on a sports event or contest if the pool is conducted for profit; or
- In a lottery conducted for profit, including the numbers game contest, policy, punch boards, and similar types of wagering.
Sports event
A sports event includes every type of amateur, scholastic, or professional sports competition, such as:
- Auto racing
- Baseball
- Basketball
- Billiards
- Bowling
- Boxing
- Cards
- Checkers
- Cricket
- Croquet
- Dog racing
- Football
- Golf
- Gymnastics
- Hockey
- Horse racing
- Lacrosse
- Rugby
- Soccer
- Squash
- Tennis
- Track
- Tug of war
- Wrestling
Contest
A contest is any competition involving speed, skill, endurance, popularity, politics, strength, or appearance.
Examples include:
- Elections
- The outcome of nominating conventions
- Dance marathons
- Log-rolling or wood-chopping contests
- Weightlifting competitions
- Beauty contests
- Spelling bees
Wagering pool
A wagering pool conducted for profit includes any method or scheme for giving prizes to one or more winning bettors based on the outcome of a sports event, a contest, or a combination or series of these events or contests if the wagering pool is managed and conducted for the purpose of making a profit.
Operators may be conducting a wagering pool or lottery for profit even if a direct profit doesn’t occur. If you operate the wagering pool or lottery with the expectation of a profit in the form of increased sales, attendance, or other indirect benefits, you conduct it for profit.
Lottery
This includes the numbers game, policy, punch boards, and similar types of wagering.
In general, a lottery conducted for profit includes any method or scheme for the distribution of prizes among persons who have paid or promised to pay for a chance to win the prizes.
The winning prizes are usually determined by the drawing of numbers, symbols, or tickets from a wheel or other container, or by the outcome of a given event.
A lottery doesn’t include either of the following kinds of events:
- Games of a type in which usually the wagers are placed, winners are determined, and the prizes are distributed in the presence of everyone who placed a wager. Examples include:
- Card games,
- Roulette games
- Dice games
- Bingo
- Keno, and
- Gambling wheels
- Drawings conducted by a tax-exempt organization, if the net proceeds of the drawing don’t benefit a private shareholder or individual.
What is not taxed?
The tax isn’t imposed on the following five items:
- Parimutuel wagering, when licensed under state law. This includes:
- Horse races
- Dog racing, and
- Jai alai
- Coin-operated devices, such as slot machines, pinball machines, or video games.
- State conducted sweepstakes, wagering pools, or lotteries, if the wager is placed with the state agency or its authorized agents or employees.
- Games of the type in which all persons placing wagers in the game are present when:
- Wagers are placed,
- Winners are determined, and
- Prizes or other property are distributed
- Drawings conducted by a tax-exempt organization under IRC Sections 501 and 521,
- As long as the net proceeds of the drawing don’t benefit a private shareholder or individual
How do I file IRS Form 730?
Send your completed return to the following address:
Department of Treasury
Internal Revenue Service
Ogden, UT 84201-0100
If you are sending payment, you may send your completed form and the tax payment together.
Video walkthrough
Watch this informative video to learn more about collecting and reporting monthly taxes on wagers using IRS Form 730.
Frequently asked questions
IRS Form 730, Monthly Tax Return for Wagers, is the tax form that taxpayers must file to report excises taxes on certain types of legal and illegal wagers. The federal government taxes legal wagers at 0.25% of the wager amount, and illegal wagers at 2.0% of the wager.
While you can pay your taxes electronically through the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System, the IRS requires taxpayers to file IRS Form 730 by paper.
The Internal Revenue Service requires taxpayers to file Form 730 monthly, even during months in which the taxpayer did not accept wagers. If you have no tax to report, you may write “None” in the entry space for Line 6, then sign and date the Form 730 before filing.
Where can I find IRS Form 730?
You can find IRS forms on the IRS website. For your convenience, we’ve enclosed the most recent official electronic version of IRS Form 730 in this article.