IRS Form 8283 Instructions
Since the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) significantly increased the standard deduction, fewer taxpayers itemize their deductions on their income tax return than ever before. For significant noncash contributions, taxpayers use IRS Form 8283 to report the value of their donations to the Internal Revenue Service.
This article will walk through IRS Form 8283 and noncash charitable contributions, specifically:
- How to complete Form 8283 to report your non-cash contributions
- How reporting noncash charitable contributions works
- Records retention requirements for charitable contributions
- IRS guidance and statistics regarding noncash contributions
Let’s start by going through this tax form, step by step.
Table of contents
How do I complete IRS Form 8283?
There are two sections to IRS Form 8283:
- Section A: Donated Property of $5,000 or Less and Publicly Traded Securities
- Section B: Donated Property Over $5,000 (Except Publicly Traded Securities, Vehicles, Intellectual Property or Inventory Reportable in Section A)
Let’s begin with the information fields above Section A.
Taxpayer information
These fields contain identifying information for both the donor, as well as any associated pass-through entities that you may be a member of.
Below is an example from the IRS instructions on how to complete these fields.
IRS example
You are an individual partner in Partnership 1, and Partnership 1 is a partner in Partnership 2.
Partnership 2 donates a noncash charitable contribution, and you are eligible to claim your share of the charitable contribution deduction.
Name(s) shown on your income tax return
Enter your name as shown on your tax return here.
Identifying number
Enter your identifying number here. This can be a Social Security number.

Entity name
Using the example cited above, enter the name of Partnership 2 here.
Entity identifying number
Using the example cited above, enter Partnership 2’s employer identification number (EIN) in this field, since this is where the noncash charitable contribution was originally reported.
Family pass-through entity
If a family pass-through entity made the noncash charitable contributions that are being reported, check the box underneath the space for the identifying number of the donating pass-through entity.
Family pass-through entities are pass-through entities in which substantially all of the interests are held, directly or indirectly, by an individual and members of the family of such individual.
For these purposes, members of the family are defined as the spouse of such individual and any individual described in IRC Section 152(d)(2)(A)–(G).
Let’s move on to Section A.
Section A: Donated Property of $5,000 or Less and Publicly Traded Securities
Complete Section A only for the following donations of property:
- Items (or a group of similar items) resulted in a total deduction of $5,000 or less
- Publicly traded securities (even if valued at more than $5,000)
- Contributions of motor vehicles (even more than $5,000)
In Section A, there is enough space for up to 4 non-cash charitable contributions, which you can enter on rows A through D. If you need to include additional information for subsequent contributions, you may attach a statement, as long as it contains similar information.
By column, we’ll go through the information that goes into each field.
Column (a)
Column (b)
If the donated property is a qualified vehicle, check the box and enter the vehicle identification number, unless a copy of IRS Form 1098-C, Contributions of Motor Vehicles, Boats, and Airplanes, is attached.
Column (c)
Provide details about the description and condition of the donated property according to the form instructions.
Vehicles
For a vehicle, enter the year, make, model, and mileage.
Securities
If you’re listing securities, enter the following:
- Company name
- Number of shares
- Kind of security
- Whether a share of a mutual fund,
- Whether regularly traded on a stock exchange or in an over-the-counter market
Real estate or tangible personal property
For real or tangible personal property, include the following information:
- Condition of the property
- Whether the donee has certified the property for its own use as an exempt organization
The condition of tangible personal property should be stated using industry standard terms or grading scales for the specific type of object, when applicable to the type of tangible personal property and when an appraisal for this property is required.
Column (d)
Enter the date of contribution for each item.

Column (e): Date acquired
If the amount of deduction for an item is $500 or less, you do not have to complete Column (e) through Column (g).
If the amount of tax deduction for an item is more than $500, then enter the month and year you acquired that particular item.
Column (f): How acquired
Enter the means by which you acquired the property. This could be by purchase, gift, inheritance, or exchange.
Column (g): Donor’s cost or adjusted basis
Enter your cost of adjusted basis, except for securities held longer than 12 months.
Column (h): Fair market value (FMV)
Enter the FMV of the property on the date you donated it. You must attach a statement if:
- You were required to reduce the FMV to figure the amount of your deduction, or
- You gave a qualified conservation contribution for which you claimed a deduction of $5,000 or less.
Members of pass-through entities
If you are a member of a pass-through entity who is filing Form 8283, enter the amount shown on your K-1 to figure the tax deduction.
Column (i): Method used to determine FMV
Enter the method that you used to determine the fair market value of the noncash contribution.
This could be any of the following methods:
- Appraisal
- Thrift shop value
- Comparable sales
- Catalog list price
IRS Publication 561, Determining the Value of Donated Property, contains additional detail.
Section B, Part I: Information on donated property
Complete this section for one item, or a group of similar items, for which you claimed a deduction of more than $5,000 per item or group, except charitable contributions reportable in Section A.
Provide a separate form for each item donated unless it is part of a group of similar items. A qualified appraisal is required for items reportable in Section B and in certain cases must be attached to Form 8283.
If the total deduction of a donated item exceeds $5,000, and is not already listed in Section A, then you must complete Section B.
Line 2: Check the appropriate box
Only check one applicable box from the following choices:
- Art (contribution of $20,000 or more)
- Qualified conservation contribution
- For certified historic structures, check this box and enter the NPS number below
- NPS number is a project number assigned by the National Park Service as part of a Historic Preservation Certification Application
- Art (contribution of less than $20,000)
- Other real estate
- Equipment
- Securities
- Collectibles
- Intellectual property
- Vehicles
- Clothing
- Digital assets
- Other
If there is more than one item, then you must complete a separate IRS Form 8283 for each type of item. Below are specific instructions by type of property.
Art valued at $20,000 or more
If your deduction for art is $20,000 or more, you must attach a complete copy of the signed appraisal to your return.
For individual objects valued at $20,000 or more, a photograph must be provided upon request. The photograph must be of sufficient quality and size (preferably an 8 x 10 inch color photograph) or a high-resolution digital image to fully show the art object.
Line 3
You must complete column (a) and column (b) (if applicable) before giving the form to the donee for completion.
Most of the columns are similar to Section A. However, differences are noted below.
Column (a)
Provide a detailed description so a lay person unfamiliar with the property could be sure the property that was appraised is the property that was contributed. The greater the value of the property, the more detail you must provide.
Qualified conservation contributions
For a qualified conservation contribution, describe the easement terms in detail, or attach a copy of the easement deed.
Donated securities
A description of donated securities should include the company name and number of shares donated. Do not include donated securities reportable in Section A.
Column (b)
If any tangible personal property or real property was donated, give a brief summary of the overall physical condition of the property at the time of the gift.
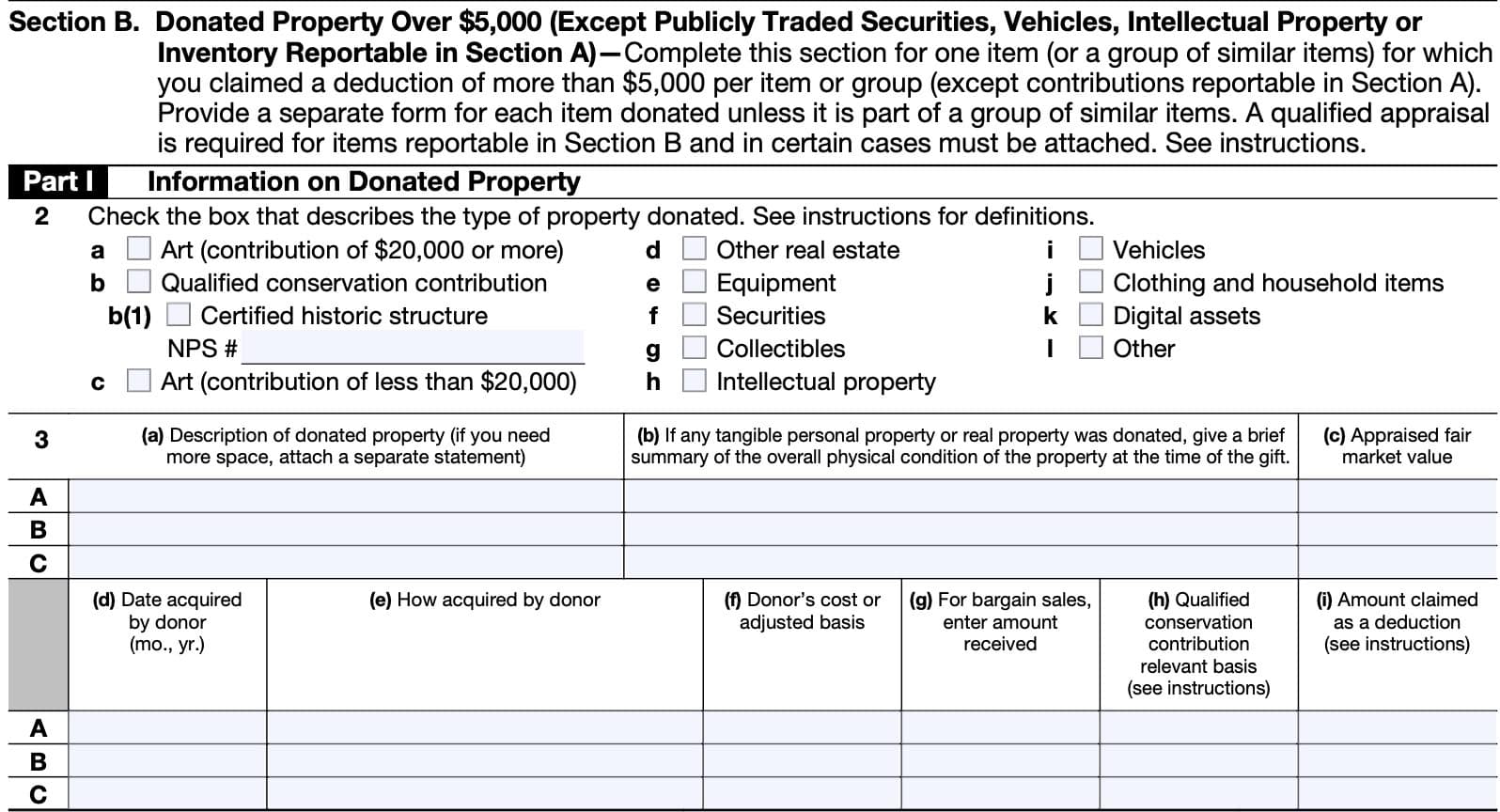
Column (c)
Include the FMV from the appraisal.
Column (d)
If you are donating a group of similar items and you acquired the items on various dates (but have held all the items for at least 12 months), you can enter “Various.” Otherwise, enter the date that you acquired the item.
Column (e)
State how you acquired the property.
This could include any of the following:
- Purchase
- Exchange
- Gift
- Inheritance
- Capital contribution
If there is a carryover basis, also include the date your predecessor acquired the property.
Column (g)
A bargain sale is a transfer of property that is in part a sale or exchange and in part a contribution. Enter the amount received for bargain sales.
Column (h) & Column (i)
Complete column (h) and (i) only if you were not required to get an appraisal, as explained earlier.
Line 4: Partial interests
Only complete this section if either of the following applies:
- You contributed less than the entire property interest listed in Part I
- You attached restrictions to the right to the income, use, or disposition of the donated property
Line 4a
Enter the letter from Section B, Part I (Line 3), which identifies the property. You must attach a separate statement for each property for which you donated less than your entire interest.
Line 4b: Total amount claimed as a deduction
In Line 4b, enter the total amount that you’ve claimed as a tax deduction for:
- The current tax year
- Any prior tax years
Line 4c
In this line, enter the name and address of each charitable organization to which you made this contribution in prior years.
However, you only need to complete this line if the name of the organization is different from the name of the donee organization listed in Part V, below.
Line 4d
In the case of donated tangible property, enter the location where the property is located.
Line 4e
Other than the donee organization, enter the name of any person who actually possesses the donated property.

Line 5: Restricted use property
Complete Lines 5a–5c only if you attached restrictions to the right to the income, use, or disposition of the donated property.
An example of a restricted use donation includes a contribution of an item to a museum on the condition that the latter does not sell the item for a specified period following the donation.
Section B, Part III: Taxpayer statement
Complete Section B, Part III, for each item included in Section B, Part I, that has an appraised value of $500 or less.
Because you may not have to show the individual value of these items in Section B, Part I, of the donee’s copy of IRS Form 8283, clearly identify them for the donee in Section B, Part III. That way the donee does not have to file IRS Form 8283 for the items valued at $500 or less.

Section B, Part IV: Declaration of Appraiser
This section includes the name, address, identifying number, and address of the appraiser. This declares that the appraiser meets all the qualified appraiser requirements previously mentioned.
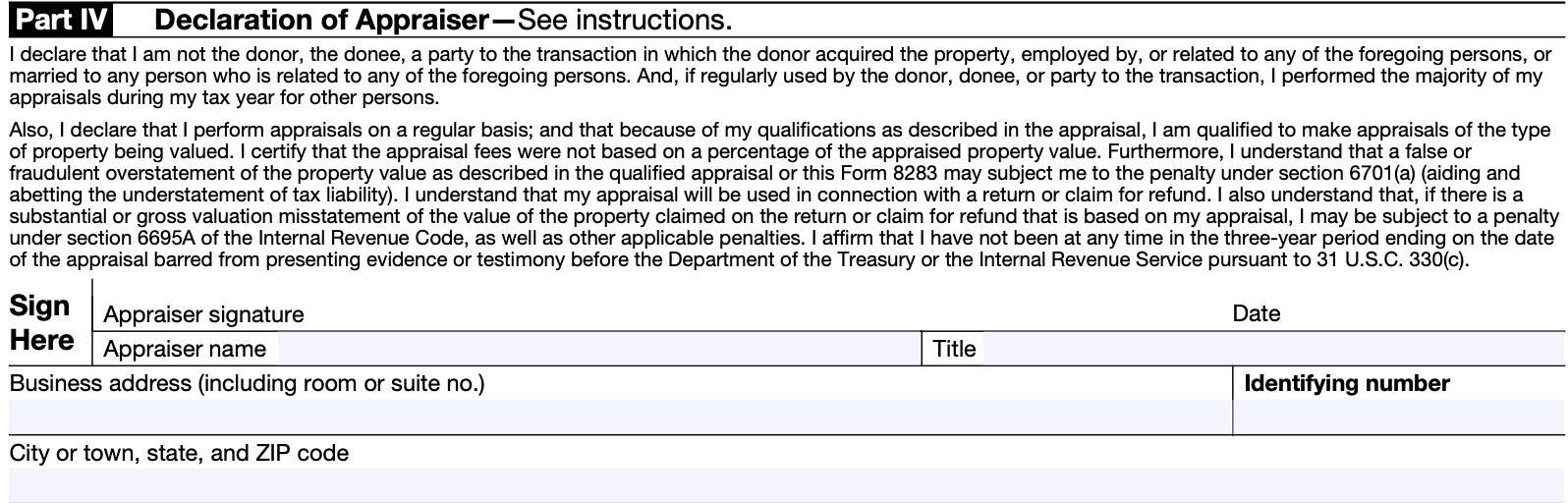
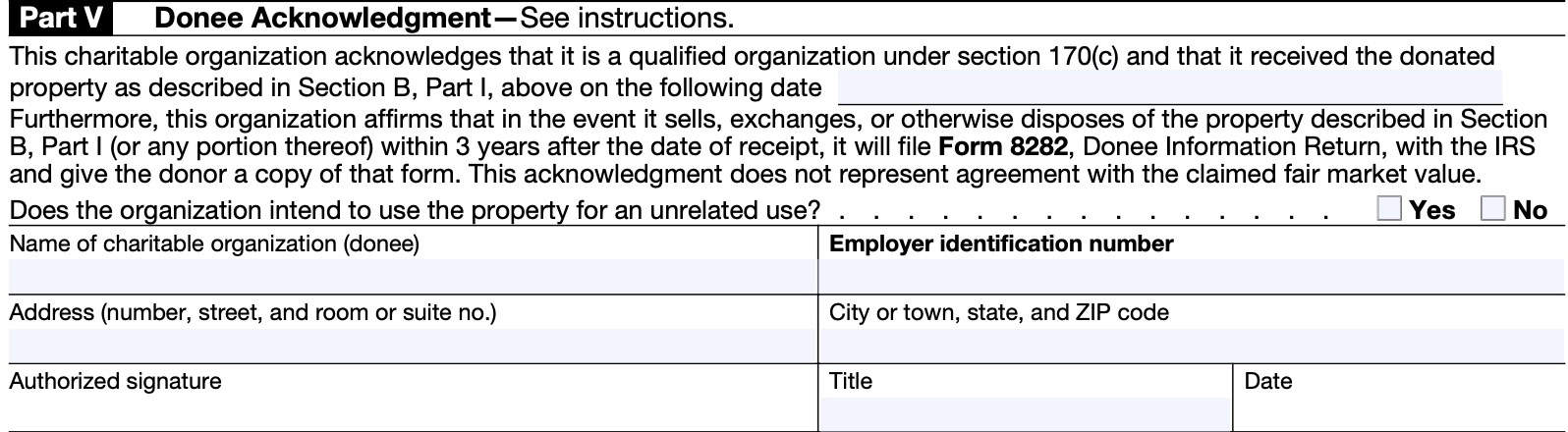
Section B, Part V: Donee acknowledgement
The person acknowledging the gift must be an official authorized to sign the tax returns of the organization, or a person specifically designated to sign IRS Form 8283.
When you ask the donee to fill out Part V, you should also ask the donee to provide you with a contemporaneous written acknowledgment required by Section 170(f)(8).
What charitable contributions do people report on IRS Form 8283?
According to 2018 IRS tax data (the latest available at the time of this writing), over 4.2 million individual taxpayers reported noncash charitable donations on Form 8283. These non-gifts represented over $70.8 billion in charitable deductions reported on Schedule A during that year.
By comparison, in 2017, the final year before TCJA took effect, 8.8 million taxpayers reported over $84 billion in deductions on Form 8283 and Schedule A on their tax returns. This represents a 52% decrease in donations but only a 16% decrease in the dollar value of donations.
It appears that there is a difference between the type of contributions people are making and the dollar value of the contributions.
What types of contributions are people making
Here are the 5 most common types of non-cash donations:
- Clothing (53.3% of donations)
- Household items (29.9%)
- Corporate stock (2.9%)
- Electronics (2.1%)
- Food items (1.7% of donations)
However, when you rank these donations in terms of dollar value, you get a different outcome:
- Corporate stock (54% of donation value carried to Schedule A)
- Clothing (9.7%)
- Easements (9.2%)
- Household items (6.7%)
- Mutual funds (3.4% of donation value)
In other words, many households donate clothing and household items. But those donations are not nearly as valuable as the dollar value of stock and other securities or land easements donated to charity. Part of that appears to be the reporting requirements involved in reporting contributed property.
How does reporting noncash charitable contributions work?
Reporting cash contributions is simple. You donate a specific amount of money, either by cash, check, or other monetary gift, receive a written acknowledgement or receipt from the charity, and keep proper records.
With a noncash charitable deduction, it can be a little trickier, depending on the dollar value of the contribution. Let’s take a look at each dollar threshold, according to IRS Publication 526, Charitable Contributions.
Noncash donations valued at less than $250
For all donations, each taxpayer should obtain a receipt, or maintain adequate records. For non-cash gifts valued at less than $250, a taxpayer doesn’t need to obtain a receipt, if it is impractical to do so. However, the taxpayer must keep records containing:
- The name and address of the qualified organization which received the contributed property
- The date and location of the charitable contribution
- A description of the property in sufficient detail under the circumstances for a layperson to understand that the description is of the contributed property (taking into account the value of the property); and
- For a security, the following information:
- Name of the issuer
- Type of security
- Whether it is publicly traded as of the date of the contribution
A security is generally considered to be publicly traded if the security is:
- Listed on a recognized stock exchange whose quotations are published daily,
- Regularly traded on a national or regional over-the-counter market, or
- Quoted daily in a national newspaper of general circulation in the case of mutual fund shares
A taxpayer’s records must also reflect the following:
- If the donated item is clothing or a household item, a description of the condition of the clothing or item.
- The fair market value of the property at the time of the contribution and
- How you figured the fair market value.
More than $250 but less than $500
For noncash gifts between $250 and $500, a taxpayer must get and keep a contemporaneous written acknowledgment of the contribution from the donee organization. For more than one contribution of $250 or more, taxpayers must have either:
- A separate acknowledgment for each, or
- One acknowledgment that shows the total contribution
What is a contemporaneous written acknowledgement?
Charitable organizations usually send written acknowledgements by January 31 of the following tax year. All acknowledgements must:
- Be in written form
- Contain the following information:
- The amount of cash contributed, if applicable
- Whether the qualified organization rendered any goods or services as a result of contribution contribution (other than certain token items and membership benefits),
- A description and good faith estimate of the value of any goods or services described. If the only benefit rendered by the organization was an intangible religious benefit, the acknowledgement must say so
To qualify as a contemporaneous written acknowledgement, the taxpayer must receive it on the earlier of the following dates:
- The date the taxpayer files their income tax return for the year of the contribution; or
- The due date, including extensions, for filing the federal tax return.
More than $500 but less than $5,000
In addition to the above, any taxpayer claiming a tax deduction of more than $500 but less than $5,000 must complete Form 8283, Section A. The completed Form 8283 must contain:
- Taxpayer’s name and taxpayer identification number
- The name and address of the qualified organization,
- The date of the contribution, and
- The following information about the contributed property:
- A description of the donated property in sufficient detail for a layperson not generally familiar with the type of property to understand that the description is of the contributed property;
- The fair market value of the property on the contribution date and the method used in figuring the fair market value;
- How the taxpayer received the property
- The approximate date the taxpayer received such property or, if created, produced, or manufactured, the approximate date the property was substantially completed; and
- The cost or other basis, and any adjustments to the basis, of property held less than 12 months and, if available, the cost or other basis of property held 12 months or more.
- Doesn’t apply to publicly traded securities.
Depending on the type of property contributed, there might be additional required information:
- In the case of real or tangible property, its condition;
- In the case of tangible personal property, whether the donee has certified it:
- For a use related to the purpose or function constituting the donee’s basis for exemption under Section 501 of the Internal Revenue Code or,
- In the case of a governmental unit, an exclusively public purpose
- In the case of securities, the following:
- Name of the issuer
- Type of securities
- Whether they were publicly traded as of the date of the contribution
Contributions over $5,000
For a noncash donation above $5,000, taxpayers must do everything above. In addition, the taxpayer must obtain a qualified appraisal conducted by a qualified appraiser, for most items.
Qualified appraisal
According to the IRS website, a qualified appraisal document is one that is:
- Made, signed, and dated by a qualified appraiser in accordance with generally accepted appraisal standards
- Meets Treasury Department standards
- Has a valuation effective date
- No earlier than 60 days before the date of the contribution, and
- No later than the date of the contribution
- For an appraisal report dated on or after the date of the contribution, the valuation effective date must be the date of the contribution; and
- Does not involve a prohibited appraisal fee.
Qualified appraiser
The IRS considers an individual to be a qualified appraiser if they meet the following criteria:
- Has earned an appraisal designation from a generally recognized professional appraiser organization, or
- Has met certain minimum education requirements and 2 or more years of experience.
- The individual regularly prepares appraisals for which he or she is paid
- The individual is not an excluded individual.
Excluded individual
The following are examples of excluded individuals
- The donor of the property or the taxpayer who claims the deduction
- The donee of the property
- A party to the transaction in which the donor acquired the property being appraised
- Unless the property is donated within 2 months of the date of acquisition and its appraised value is not more than its acquisition price.
- This applies to the person who sold, exchanged, or gave the property to the donor, or any person who acted as an agent for the transferor or donor in the transaction.
- Any person employed by any of the above persons.
- Any person related under Internal Revenue Code Section 267(b) to any of the above, or someone married to a person related to any of the above persons
- An appraiser who appraises regularly for a related party, as described above, and who does not perform a majority of his or her appraisals made during his or her tax year for other persons
- An individual who receives a prohibited appraisal fee for the appraisal of the donated property. Generally, a fee structured as a percentage of the overall value is a prohibited fee
- An individual who is prohibited from practicing before the IRS under Section 330(c), Title 31 of the United States Code at any time during the 3-year period prior to the appraisal date.
Qualified appraiser exceptions
A qualified appraisal is not required for contributions of:
- Qualified vehicles for which you obtain a contemporaneous written acknowledgement
- Certain inventory
- Publicly traded securities, or
- Certain intellectual property
You must keep all qualified appraisals in your records and submit IRS Form 8283 with your income tax return.
Art contributions over $20,000
If the amount of donated art exceeds $20,000, you must attach a complete copy of the signed written appraisal to your tax return.
Contributions over $500,000
In addition to the above, for contributions over $500,000, a copy of each qualified appraisal must accompany the completed tax return. Treasury Regulations Section 1.170A-16 contains more information.
Video walkthrough
Do you use TurboTax?
If you don’t, is it because the choices are overwhelming to you?
If so, you should check out our TurboTax review page, where we discuss each TurboTax software product in depth. That way, you can make an informed decision on which TurboTax offering is the best one for you!
Click here to learn more about which TurboTax option is best for you!
Frequently asked questions
Taxpayers use IRS Form 8283 to report noncash charitable contributions to the Internal Revenue Service. Do not use Form 8283 to report out-of-pocket expenses for volunteer work or amounts you gave by check or credit card. Treat these items as cash contributions.
Individual taxpayers submit IRS Form 8283 with their federal income tax return. If you submit your tax return electronically, you must also submit IRS Form 8283 via electronic means.
To meet the minimum education requirement, the individual must have successfully completed professional or college-level coursework obtained from a professional or college-level educational organization, trade or appraiser organization, or as part of an apprenticeship program through his or her employer.
Where can I find a copy of IRS Form 8283?
You can download a copy of this and other tax forms on the IRS website. Otherwise, you may download a copy of Form 8283 by selecting the file below.
Related tax forms
This tax form is one of the fillable tax forms provided by the Internal Revenue Service, to help taxpayers reduce their tax preparation costs. To see more forms like this, visit our free fillable tax forms page, where you’ll also find articles like this.
Unlike the IRS, our articles contain step by step instructions for each tax form, as well as video walkthroughs. You can also check out all of our videos by subscribing to our YouTube channel!